- contact
 Samved Orthopaedic Hospital
Samved Orthopaedic Hospital
"Samved" Hospital
3rd Floor, Near Sopan Flats, On Stadium Circle to Commerce College Six Roads, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad - 380 009.
Tel: +91 79 2656 2993
Email: samvedortho@yahoo.com

Total Hip Replacement - Hip Replacement Surgery
Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided to undergo hip replacement surgery, this information will help you understand the benefits and limitations of total hip replacement. This article describes how a normal hip works, the causes of hip pain, what to expect from hip replacement surgery, and what exercises and activities will help restore your mobility and strength, and enable you to return to everyday activities.
If your hip has been damaged by arthritis, a fracture, or other conditions, common activities such as walking or getting in and out of a chair may be painful and difficult. Your hip may be stiff, and it may be hard to put on your shoes and socks. You may even feel uncomfortable while resting.
If medications, changes in your everyday activities, and the use of walking supports do not adequately help your symptoms, you may consider hip replacement surgery. Hip replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure that can relieve your pain, increase motion, and help you get back to enjoying normal, everyday activities.
First performed in 1982, Dr. Bharat Patel is a pioneer in the field of hip replacement in the western region of india. Since then, improvements in joint replacement surgical techniques and technology have greatly increased the effectiveness of total hip replacement.
Anatomy
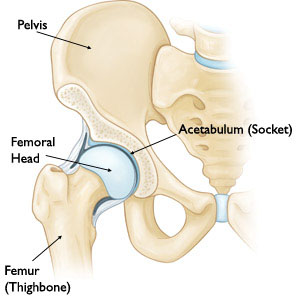
The hip is one of the body's largest joints. It is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part of the large pelvis bone. The ball is the femoral head, which is the upper end of the femur (thighbone).
The bone surfaces of the ball and socket are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth tissue that cushions the ends of the bones and enables them to move easily.
A thin tissue called synovial membrane surrounds the hip joint. In a healthy hip, this membrane makes a small amount of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates almost all friction during hip movement.
Bands of tissue called ligaments (the hip capsule) connect the ball to the socket and provide stability to the joint.
Common Causes of Hip Pain
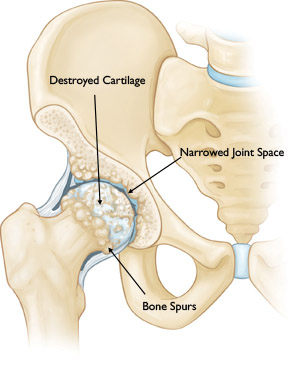
The most common cause of chronic hip pain and disability is arthritis. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic arthritis are the most common forms of this disease.
Osteoarthritis. This is an age-related "wear and tear" type of arthritis. It usually occurs in people 50 years of age and older and often in individuals with a family history of arthritis. The cartilage cushioning the bones of the hip wears away. The bones then rub against each other, causing hip pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis may also be caused or accelerated by subtle irregularities in how the hip developed in childhood.
Rheumatoid arthritis. This is an autoimmune disease in which the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and thickened. This chronic inflammation can damage the cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common type of a group of disorders termed "inflammatory arthritis."
Post-traumatic arthritis. This can follow a serious hip injury or fracture. The cartilage may become damaged and lead to hip pain and stiffness over time.
Avascular necrosis. An injury to the hip, such as a dislocation or fracture, may limit the blood supply to the femoral head. This is called avascular necrosis. The lack of blood may cause the surface of the bone to collapse, and arthritis will result. Some diseases can also cause avascular necrosis.
Childhood hip disease. Some infants and children have hip problems. Even though the problems are successfully treated during childhood, they may still cause arthritis later on in life. This happens because the hip may not grow normally, and the joint surfaces are affected.
Description
In a total hip replacement (also called total hip arthroplasty), the damaged bone and cartilage is removed and replaced with prosthetic components.
- The damaged femoral head is removed and replaced with a metal stem that is placed into the hollow center of the femur. The femoral stem may be either cemented or "press fit" i.e Uncemented into the bone.
- A metal or ceramic ball is placed on the upper part of the stem. This ball replaces the damaged femoral head that was removed.
- The damaged cartilage surface of the socket (acetabulum) is removed and replaced with a metal socket. Screws or cement are sometimes used to hold the socket in place.
- A plastic, ceramic, or metal spacer is inserted between the new ball and the socket to allow for a smooth gliding surface.
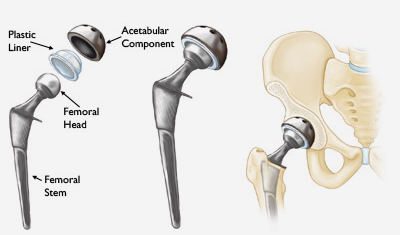
(Left) The individual components of a total hip replacement. (Center) The components merged into an implant. (Right) The implant as it fits into the hip.
- The damaged femoral head is removed and replaced with a metal stem that is placed into the hollow center of the femur. The femoral stem may be either cemented or "press fit" i.e Uncemented into the bone.
- A metal or ceramic ball is placed on the upper part of the stem. This ball replaces the damaged femoral head that was removed.
- The damaged cartilage surface of the socket (acetabulum) is removed and replaced with a metal socket. Screws or cement are sometimes used to hold the socket in place.
- A plastic, ceramic, or metal spacer is inserted between the new ball and the socket to allow for a smooth gliding surface.
(Left) The individual components of a total hip replacement. (Center) The components merged into an implant. (Right) The implant as it fits into the hip.
Is Hip Replacement Surgery for You?
The decision to have hip replacement surgery should be a cooperative one made by you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopaedic surgeon. The process of making this decision typically begins with a referral by your doctor to an orthopaedic surgeon for an initial evaluation.
Candidates for Surgery
There are no absolute age or weight restrictions for total hip replacements.
Recommendations for surgery are based on a patient's pain and disability, not age. Most patients who undergo total hip replacement are age 50 to 80, but orthopaedic surgeons evaluate patients individually. Total hip replacements have been performed successfully at all ages, from the young teenager with juvenile arthritis to the elderly patient with degenerative arthritis.
When Surgery Is Recommended
There are several reasons why your doctor may recommend hip replacement surgery. People who benefit from hip replacement surgery often have:
- Hip pain that limits everyday activities, such as walking or bending
- Hip pain that continues while resting, either day or night
- Stiffness in a hip that limits the ability to move or lift the leg
- Inadequate pain relief from anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, or walking supports
Deciding to Have Hip Replacement Surgery
Talk With Your Doctor
Your orthopaedic surgeon will review the results of your evaluation with you and discuss whether hip replacement surgery is the best method to relieve your pain and improve your mobility. Other treatment options — such as medications, physical therapy, or other types of surgery — also may be considered.
In addition, your orthopaedic surgeon will explain the potential risks and complications of hip replacement surgery, including those related to the surgery itself and those that can occur over time after your surgery.
Never hesitate to ask your doctor questions when you do not understand. The more you know, the better you will be able to manage the changes that hip replacement surgery will make in your life.
Realistic Expectations
An important factor in deciding whether to have hip replacement surgery is understanding what the procedure can and cannot do. Most people who undergo hip replacement surgery experience a dramatic reduction of hip pain and a significant improvement in their ability to perform the common activities of daily living.
With normal use and activity, the material between the head and the socket of every hip replacement implant begins to wear. Excessive activity or being overweight may speed up this normal wear and cause the hip replacement to loosen and become painful. Therefore, most surgeons advise against high-impact activities such as running, jogging, jumping, or other high-impact sports.
Realistic activities following total hip replacement include unlimited walking, swimming, golf, driving, hiking, biking, dancing, and other low-impact sports.
With appropriate activity modification, hip replacements can last for many years.
Recovery after Surgery
The success of your surgery will depend in large measure on how well you follow your orthopaedic surgeon's instructions regarding home care during the first few weeks after surgery.
Wound Care
You may have stitches or staples running along your wound or a suture beneath your skin. The stitches or staples will be removed approximately 2 weeks after surgery.
Avoid getting the wound wet until it has thoroughly sealed and dried. You may continue to bandage the wound to prevent irritation from clothing or support stockings.
Diet
Some loss of appetite is common for several weeks after surgery. A balanced diet, often with an iron supplement, is important to promote proper tissue healing and restore muscle strength. Be sure to drink plenty of fluids.
Activity
Exercise is a critical component of home care, particularly during the first few weeks after surgery. You should be able to resume most normal light activities of daily living within 3 to 6 weeks following surgery. Some discomfort with activity and at night is common for several weeks.
Your activity program should include:
- A graduated walking program to slowly increase your mobility, initially in your home and later outside
- Resuming other normal household activities, such as sitting, standing, and climbing stairs
- Specific exercises several times a day to restore movement and strengthen your hip. You probably will be able to perform the exercises without help, but you may have a physical therapist help you at home or in a therapy center the first few weeks after surgery





